Navigating the IoT Connectivity Landscape: A Guide to LPWAN Technologies
Intro
Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technologies have emerged as a vital component of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. They cater to the connectivity needs of devices and applications that require long-range communication, extended battery life, and cost-efficient data transmission. Key LPWAN use cases include smart cities, smart meters, remote & environmental monitoring, industrial monitoring & automation, health monitors, wearables, and asset tracking.
Background
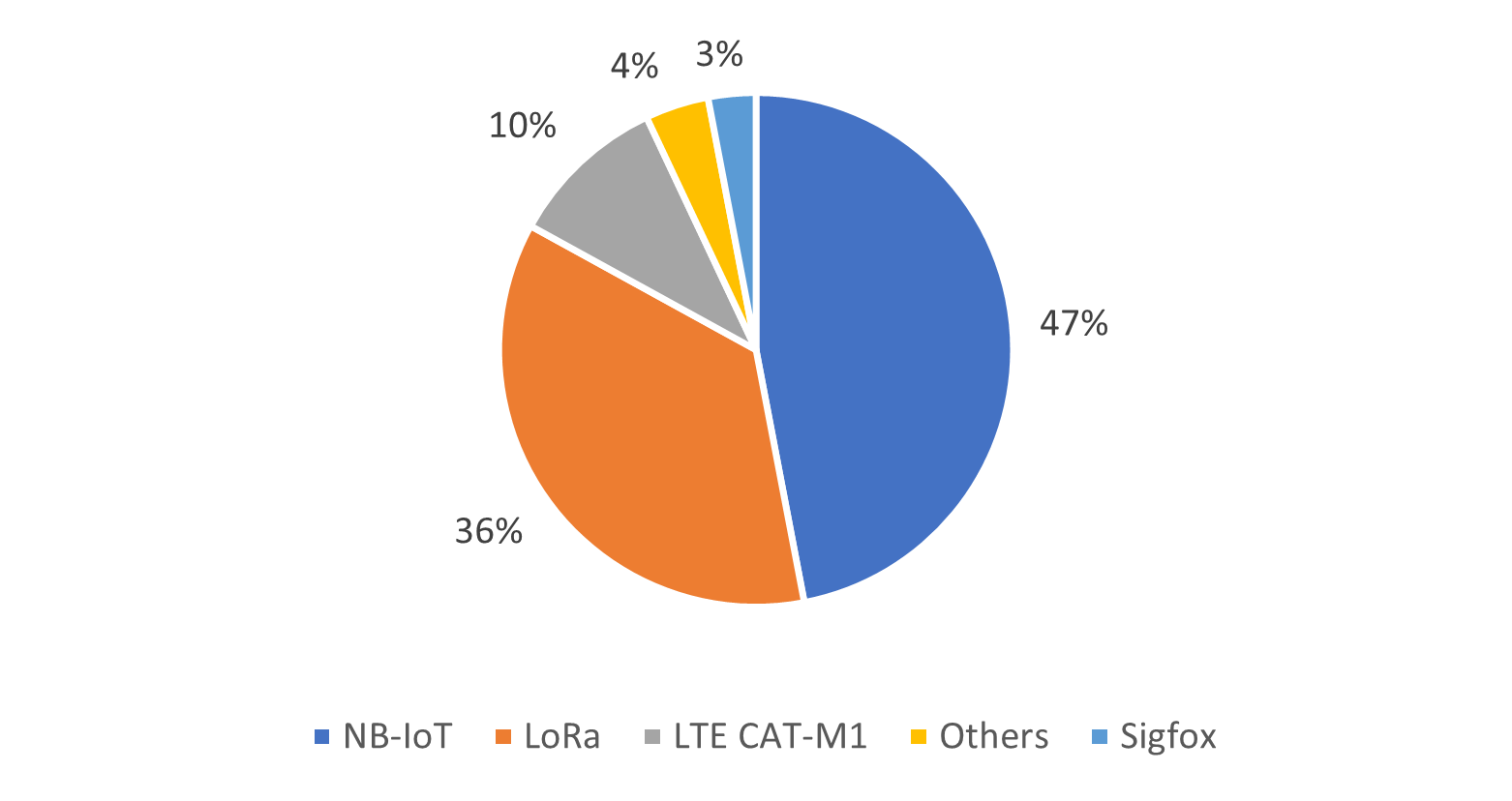
Leading LPWAN technologies include NB-IoT, LTE CAT-M1, Sigfox, and LoRaWAN. Other LPWAN technologies include Weightless, RPMA, and MIOTY. IoT Analytics estimated that NB-IoT and LoRa accounted for 83% of the 2021 LPWAN market.
LPWAN Technology Comparison & Descriptions
Key decision factors for selecting the right LPWAN technology for a specific use case include available bandwidth, data speed/throughput, range, power consumption, and cost.
|
|
Cellular | Non-Cellular | ||
|
|
NB-IoT | LTE-CAT M1 | Sigfox |
LoRaWAN |
|
Spectrum |
Licensed |
Unlicensed |
||
|
Bandwidth |
200kHz | 1.4MHz | 0.1kHz |
125-500kHz |
|
Throughput |
200kbps | 1mbps | 0.1kbps |
50kbps |
|
Range |
Up to 10km | Up to 10km | Up to 50km |
Up to 20km |
| Power Consumption |
Low-to-Moderate |
Moderate |
Extremely Low |
Ultra-Low |
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
NB-IoT is a cellular technology optimized for low-power, wide-area IoT applications. It operates in the licensed spectrum, providing better security and quality of service compared to unlicensed LPWAN options. NB-IoT offers deep coverage and improved indoor penetration, making it suitable for applications like smart cities, agriculture, and industrial monitoring. Its low data rates and power consumption enable devices to operate for years on a single battery.
LTE CAT-M1
LTE CAT-M1 is a cellular technology that operates within existing LTE networks, offering enhanced coverage and better penetration compared to traditional cellular networks. LTE CAT-M1 supports both voice and data services, making it suitable for a wide range of IoT applications such as smart meters, wearables, and asset tracking. It provides a balance between data rate, coverage, and power consumption, making it suitable for applications that require reliable connectivity and extended battery life.
Sigfox
Sigfox is a proprietary LPWAN technology that operates in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) band. It utilizes ultra-narrowband modulation to transmit small amounts of data over long distances. Its technology is suitable for applications requiring sporadic, low-bandwidth data transmission, such as asset tracking, environmental monitoring, and smart agriculture.
SigFox filed for bankruptcy in January 2022. In April 2022, Singapore-based IoT network firm, Unabiz, acquired Sigfox and its French network operations for a reported €25 million. Since acquiring Sigfox, UnaBiz has opened the technology to align with its positioning as a tech-agnostic service provider and integrator. In April 2023, Unabiz shared they had activated 1.6 million new devices in the last 12 months, bringing the total connected devices to 11.4 million.
LoRaWAN
LoRa technology was developed in 2009. The LoRa Alliance was founded in 2015 and the network protocol was named LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network). LoRaWAN is an open standard technology that operates in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz ISM band. It employs chirp spread spectrum modulation to provide long-range coverage and is known for its flexibility in terms of deployment models – public, private, or community networks.
LoRaWAN is primarily used in applications like smart cities, smart buildings, and industrial automation. In March 2021, it was estimated there were 178 million devices connected to over 140 public and private LoRa networks globally.
Other LPWAN Technologies
Weightless: An open standard that offers both wide-area and local-area coverage, suitable for industrial and smart city applications.
RPMA: Random Phase Multiple Access (RPMA) utilizes the unlicensed, globally available 2.4 GHz ISM band for long-range, low-power communication. RPMA, developed by Ingenu, is primarily used for smart grids and remote monitoring applications.
MIOTY: Based on Telegram Splitting Ultra Narrowband (TS-UNB) technology, MIOTY boasts robustness against interference and is ideal for applications in noisy environments.
Other companies leveraging LPWAN technology to address specific use cases include Nwave (smart parking), Telensa (smart streetlights) and Helium (decentralized wireless IoT network tied to the cryptocurrency Helium Network Token).
Positioning Universal’s LPWAN View
Positioning Universal’s mobile IoT hardware portfolio extensively uses LTE CAT-M1 cellular technology with several devices offering both NB-IoT and LTE CAT-M1 connectivity.
LTE CAT-M1 combines accurate tracking and monitoring with reliable data communication over cellular networks. This synergy ensures seamless tracking of vehicles and assets using LTE CAT-M1’s high bandwidth capability, fast data speeds, and extended coverage.
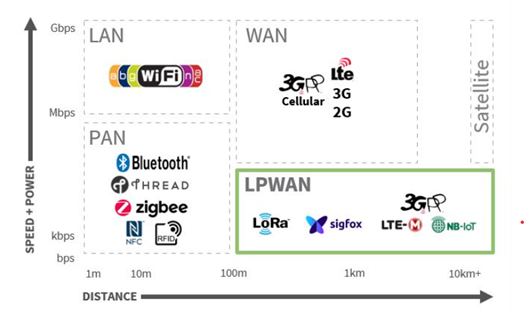
Source: Allion



Leave a Reply